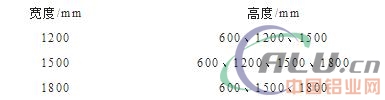
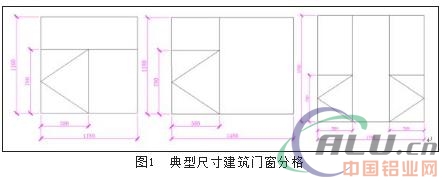
[China Aluminum Network] Assembly Building Overview Prefabricated buildings, or integrated buildings, are prefabricated at the factory with some or all of the components of the building, and then transported to the construction site where the components are assembled by means of a reliable connection. In Europe, America and Japan, it is called an industrialized or industrialized house. Prefabricated houses are currently divided into three main categories: prefabricated reinforced concrete structures, light steel structures, and prefabricated container houses. (1) Precast reinforced concrete structures. Prefabricated concrete structure is based on precast concrete components as the main components, after assembly, connection, combined with part of the cast-in-place concrete structure. The PC component is a finished concrete component formed by factory fabrication of a component processing company. PC homes have many advantages such as high efficiency, energy saving, environmental protection, cost reduction, and providing residential functions and performance. (2) Light steel structure. The light steel housing is characterized by excellent features such as light weight, large span, good wind and seismic performance, thermal insulation, sound insulation and other indicators. It is a green building system that is efficient, energy-saving, environmentally friendly, and consistent with the principle of sustainable development. Applicable to villas, multi-storey houses, resorts and other civil buildings and building layers, roofs, etc. Pre-assembled walls include pre-installed exterior wall cladding, insulation and windows. (3) Prefabricated container houses. The container is used as the basic module, and the manufacturing mode is adopted. In the factory, the structure construction and interior decoration of each module are completed in the assembly line and then transported to the project site. The different types of houses are quickly assembled according to different purposes and functions. Prefabricated buildings have the following characteristics: (1) Functional integration. Prefabricated buildings integrate good functions such as energy saving, sound insulation, fire protection, and facades. The use of a good insulation performance of the external protection structure can reduce winter heating energy consumption and summer air conditioning energy consumption in winter; insulation materials and multi-layer glass have better sound absorption and sound insulation function, can reduce external noise as much as possible, provide quiet Indoor environment; prefabricated buildings use non-combustible or non-flammable materials, with good fire performance; appearance is fresh and durable. Facade facade is relatively fresh, not easily deformed, cracked and faded. (2) Industrialization of production. The exterior wall panels in prefabricated buildings are produced at the production plant through molds, which is different from the traditional on-site cast-in-place concrete methods and can realize the assembly line production of exterior wall panels. Assembled building doors and windows openings are modularized and manufactured by the factory. Therefore, doors and windows can be directly produced in accordance with the drawings, and the industrialization of door and window products can be realized. (3) Construction and assembly. The corresponding components are produced at the production plant and then transported to the construction site where professionals install and splice at the site. The construction speed is quick, the construction period can be shortened; the construction workers on the construction site are reduced, the construction work is more convenient and orderly, the labor intensity of the workers is reduced; the waste, waste water and noise at the construction site are reduced, the environmental pollution is reduced, and the energy conservation and emission reduction are performed; each process is performed Like equipment can be installed, requiring accuracy, quality assurance; can also reduce construction costs. The United States began implementing accessories construction and mechanized production during the energy crisis of the 1970s. Urban residential structure in the United States is basically based on factory-built concrete assembly and steel assembly, and has formed a series of strict industry standard specifications. The "PCI Design Handbook" compiled by the United States-based Prefabricated and Prestressed Concrete Association PCI includes related parts of the fabricated structure and has extensive influence in the United States and internationally. European assembly construction developed earlier. France has implemented the construction of prefabricated concrete buildings since 1891. It has a history of 130 years. The industrialization of French buildings is mainly composed of concrete systems, supplemented by steel and wood structural systems. The prefabricated houses in Germany mainly use laminated plates, concrete and shear wall structure systems. As a country with rapid development of energy-saving buildings in the world and first proposed passive building concepts, its energy-saving buildings and passive buildings have adopted assembly-type construction methods. The standards and energy efficiency standards have been fully integrated. Sweden and Denmark had already developed prefabricated components such as concrete and slabs as early as the 1950s. At present, the number of common components in new houses has reached 80%, achieving unity and standardization. There are already typical EU standards, such as EN 1992-1-1 "European Regulations: Design of Concrete Structures - Part 1-1: General Regulations and Architectural Design Regulations" and EN 13369 "Standardization of Precast Concrete Component Quality". Japan introduced the concept of prefabricated housing in 1968. In 1990, it adopted the componentized and factory-based production methods. From the very beginning, it pursued the fitting production system of high-rise residential buildings to meet the needs of the densely populated housing market in Japan. A series of policies and policies form a unified modular standard, which resolves the contradiction between standardization, mass production, and diversified demand. Singapore has developed 15 to 30-story unitized prefabricated housing, accounting for more than 80% of the country's total residential housing. The standardization is achieved through the planar layout, component dimensions and the repeatability of the installation nodes. The design is the core, and the industrialization of design and construction is mutually compatible. The assembly rate reaches over 70%. In the 1970s, prefabricated buildings began to slowly spread in China; in the 1980s, prefabricated roof beams, prefabricated roof panels and other components were also used in some projects, but were limited by the technical level and the construction quality was poor. For example, the sealing effect of the roof panel is not good, and the waterproof measures are not perfect, resulting in the phenomenon of water leakage and poor sound insulation. In the 1990s, great progress was made in construction technology and management. Prefabricated buildings were mentioned and further developed. In 2013, the General Office of the State Council issued the “Notice of the General Office of the State Council on Transmitting the Action Plan for Green Building of the National Development and Reform Commission, the Ministry of Housing, and Urban-Rural Development†(Guobanfa (2013) No. 1), of which (8) In order to promote the industrialization of buildings, the departments of housing and urban and rural development should speed up the establishment of standards systems that promote the industrialization of construction, such as design, construction, and parts production, promote the standardization of structural components, parts, and components, enrich the types of standard parts, and increase versatility and availability. Replacement. Promote prefabricated concrete, steel structures and other building systems that are suitable for industrial production, speed up the development and construction of prefabrication and assembly technologies, and increase the level of industrialization technology integration of buildings. Support the construction of an industrialized base that integrates design, production, and construction, and conduct pilot demonstrations of industrialized buildings. Actively promote the full renovation of residential buildings to encourage new residential renovations in place or menu-style renovation, and promote the integration of personalized decoration and industrial decoration. In January 2014, the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development Notice required all localities to actively promote the work of green housing, and at the same time released the "Technical Guidelines for Green Safe Housing" (for trial implementation) (hereinafter referred to as the "Guidelines"). Formulate green and affordable housing technology policies in the region and do a good job of technical guidance. There are eight items in the “Guidelineâ€, which emphasizes the basic principles that green affordable housing should follow, research and formulate a green protection housing index system, and propose technologies such as the planning, design, construction, and industrialization of green affordable housing. Points. In addition, the "Guidelines" also set specific industrialization technical indicators and systematized technologies. To provide effective and effective protection for a large number of rapid residential developments, and to fundamentally promote green building initiatives. On September 12, 2017, the State Council issued the Guiding Opinions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China on Launching Quality Improvement Actions, and the “Opinions†clearly stated that “in accordance with local conditions, the building energy efficiency standards should be improved. The standards for green building materials should be improved and the production and use of green building materials should be promoted. We will vigorously develop prefabricated buildings, improve the quality and safety performance of building decoration parts, and promote the construction of green ecological communities." At present, many cities in China have formulated assembly-type building development plans. Taking Beijing as an example, by 2018, it will be necessary to achieve a ratio of more than 20% of the total new building area of ​​fabricated buildings, and to achieve more than 30% of the total new building area by 2020. Shanghai Municipality implements the control of “two mandatory ratios†(heading ratio of prefabricated buildings and prefabrication rate of newly-built prefabricated building units) at the source of the land, ie, the total construction area of ​​prefabricated buildings was implemented in 2015. The percentage of new civil buildings that meet the conditions within the Outer Ring Road in 2016 is not less than 50%. All of the newly-built civil buildings in 2016 will use prefabricated buildings, which exceeds 50% outside the outer loop. From 2017 onwards, the outer loop will increase year by year on a 50% basis. By 2020, Jiangsu province will achieve the target of more than 30% of the province's newly-built buildings. In addition, Guangdong, Zhejiang, Hubei, Shandong, Hunan, Sichuan, Hebei, Anhui, Fujian, Hainan, Henan, Gansu, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Jiangxi, Jilin, Guizhou, Yunnan, and more than 20 provinces and cities proposed prefabricated building development. The goal is that the prefabricated building has ushered in a major development in China. 2 Prefabricated Building Standard Requirements for Doors and Windows At present, China's published assembly building technical standards are: GB/T "prefabricated concrete construction technical standards", GB/T "prepared steel construction technology standards" and GB/T "Technical Standards for Prefabricated Wooden Structures". All three standards were formally implemented on June 1, 2017. GB/T "Technical Standards for Assembled Concrete Buildings" is applicable to the design, production, transportation, construction, installation, and quality acceptance of prefabricated concrete buildings with seismic intensity of 8 degrees and below; GB/T. "Technical Standard for Assembled Steel Structure Buildings" is applicable to the design, production, transportation, construction and installation, quality inspection and use and maintenance of prefabricated steel structure buildings with seismic intensity of 6 degrees to 9 degrees; GB/T "Assembled wood" The Technical Standards for Structural Buildings are applicable to the design, manufacture, construction, acceptance, use and maintenance of prefabricated timber-framed buildings with seismic intensity of 6 degrees to 9 degrees. In addition, there are more than 80 related national standards, atlases, industry standards, and local standards concerning assembly building design, production, construction, and acceptance. The special requirements related to doors and windows of prefabricated building technology standards mainly include five aspects: coordination of openings, modularization of design, integration of functions, installation and assembly, and management and control information. Other related design, manufacture, installation, and acceptance are basically the same as those of traditional door and window products. 2.1 Coordination of Opening Modulus In the standard, the requirements for the door opening and opening moduli are clearly stated: “... The width of the door and window openings should adopt the horizontal expansion module series 2 nM, 3 nM (n is a natural number).†“... The height of the door and window openings should be vertical. Expand the module number nM. "The size design of the door and window parts should comply with the current national standard "Building doors and windows opening size series" GB/T 5824 and "Building doors and windows opening size coordination requirements" GB/T 30591 requirements." The size of openings in doors and windows should comply with the modulus regulations. According to GB/T “Building Modulus Coordination Standardsâ€, the basic module has a value of 100 mm (1 M equals 100 mm), and the entire building and part of the building and the modular dimensions of the building components should be Is a multiple of the basic modulus. The export modulus is divided into the expansion modulus and the number of modules, the expansion of the modulus base should be 2M, 3M, 6M, 9M, 12M ..., the submodule base should be M/10, M/5, M/2. According to this regulation, the width of the door and window openings shall be an integral multiple of 200 mm and 300 mm, and the height of the opening shall be an integral multiple of 100 mm. According to the principle of less specifications and multiple combinations, the opening and closing module of doors and windows is recommended to be further expanded to an integer multiple of 3M, namely 3M, 6M, 9M, 12M, 15M and 18M. 2.2 Design Standardization The standard for the standard design of assembled building doors and windows is as follows: “Assembly building should adopt the design method of combination of modules and modules, follow the principle of less specifications and multiple combinations, and realize serialization and diversification of building and parts parts.†The prefabricated building facade design should meet the following requirements: ... The exterior windows and other parts and components should be standardized. "The external doors and windows should use the standardized series of products produced in the factory, and use the outer doors and windows with the water board and other supporting series. "Parts." "The tolerances of the part sizes and mounting positions shall be determined in accordance with the production assembly requirements, the deformation of the main structure, the deformation capability of the sealing material, the material shrinkage, temperature difference deformation, and construction errors." It can be seen that the standardization of door and window design should be conducted from the following aspects: The first is the standardization of the size of doors and windows. The size of the door and window products should be reduced by the corresponding hole size to ensure normal installation. The traditional installation method of doors and windows is divided into wet installation and dry installation. Wet installation refers to installation without a frame, and dry installation refers to installation using a frame. The installation of prefabricated building doors and windows can also be divided into unboxed installations and boxed installations, where the attachments can be divided into pre-embedded frames and post-attached frames. In the case of frameless installation and embedded frame installation, the size of the opening is the standard size of the opening, and the size of the opening can be reduced. When the rear frame is installed, the size of the attached frame should also be reasonably reduced. Followed by the standardized grid. One of the more important considerations in the partitioning of doors and windows is to open the fan, so it is recommended to first determine the size of the opening fan. For casement windows, it is recommended that the grid width be 600 mm and the height be 800 mm, 1000 mm, 1200 mm. The other divisions can be determined based on the size of the opening fan. The standardization of the installation structure is later. For prefabricated buildings, it is recommended to give priority to the installation of pre-embedded frames. 2.3 Function Integration Assembly-type building doors and windows, as external building protection components, should integrate the main functions that traditional building doors and windows should undertake. The standard stipulates: “The external protection system should be based on the climatic conditions of the region where the assembly building is located, and the use of functions, etc., to determine the wind resistance, seismic performance, impact resistance, fire performance, water tightness, airtightness, sound insulation, and heat. Work performance and durability requirements." For the assembly of building doors and windows, should be comprehensively considered its wind pressure performance, air tightness, watertightness, insulation, shading, sound insulation, lighting performance, durability, fire performance. Therefore, the above performance should be comprehensively considered when designing building-type doors and windows, and performance and function design should be carried out according to the requirements of various regions. 2.4 Construction Assembling The standard stipulates: “Parts of prefabricated buildings shall use standardized interfaces.†“The external doors and windows shall be securely connected. The airtight performance, watertight performance and heat preservation performance of the joints between the door and window openings and the outer door and window frames shall not be lower than those related to the external doors and windows. Performance." "Prefabricated external walls, doors and windows should be fixed by means of prefabricated or prefabricated parts. External doors and windows can be pre-installed or post-installed and meet the following requirements: (1) When prefabricating method is used, external doors and windows should be In the factory and the prefabricated exterior wall forming; 2 using the post-installation method, the prefabricated exterior doors and windows openings should be set embedded parts." The “pre-installation method†mentioned in the standard stipulates that the outer door and window frames should be integrally formed at the factory with the prefabricated outer wall. This means that the window frame is embedded directly in the outer wall. This practice will cause the replacement of the outer window to be difficult and is not recommended. . The installation method for prefabricated building doors and windows is recommended to adopt the “post-installation method†proposed in the standard, that is, the method of installing embedded parts at the entrance of the external wall. This method is convenient for door and window replacement. 2.5 Management and Control Information The standard stipulates: "Assembly-type architectural design should adopt building information model (BIM) technology, establish an information-based collaborative platform, use standardized information modules such as function modules, parts and components, unify coding, unify rules, and share data information with the entire profession to realize construction. The whole process of management and control." As an important part of prefabricated buildings, building doors and windows should also establish a unified code, unified rules of the information base. The information library should be able to give the size of the opening, the size of the outer window, and the performance information of the grid and the outer window, etc., for the architect to use. 3 Assembled building requirements for doors and windows industry Assembled building requires the coordination of modularity of doors and windows, design standardization, function integration, construction and assembly and management and control information. The building doors and windows industry should adapt to this trend, and it is also the five major advantages of the door and window industry, including the following aspects. 3.1 Serialization and standardization of door and window products The serialization and standardization of door and window products should begin with the standardization and serialization of the openings. The first is to simplify the size selection of doors and windows from the perspective of architectural design. Table 1 Assembly building doors and windows opening size Then the standard size of the door and window is determined according to the installation method. The prefabricated building is proposed to adopt the method of pre-embedding the frame. It is clear that the internal dimensions of the attached frame are used as the unified coordination position of the two parties, and the accuracy of the opening of the box is standardized. The hole size is shown in Table 1. The error can be controlled within ±1 mm. The size of the door and window corresponding to the size of the opening can be determined. See Table 2. Table 2 Reference Standard Size of Assembled Building Doors and Windows After the door and window size is determined, the window and door can be determined. It is generally recommended that the open window size of the hinged windows and doors be at least 580 mm in width and at least 780 mm in height. Typical architectural doors and windows are shown in Figure 1. 3.2 Factory production of doors and windows Traditional building doors and windows production is completed in the factory all components such as doors and windows frames, in accordance with the construction schedule requirements of the box, fan, glass factory shipped to the construction site installation, leading to the door and window later critical assembly procedures were forced to complete at the site, the factory can not be finished Inspection, it is difficult to ensure product quality. For prefabricated buildings, the model of the assembly factory is encouraged. The factory will transport all assembled doors and windows that have passed the inspection to the prefabrication project, and the one-time installation is completed to ensure the quality of the doors and windows. 3.3 Door and Window Construction Assembling The installation of prefabricated building doors and windows will be developed towards an integrated installation. At present, the installation of prefabricated building doors and windows in China is basically the same as the traditional box-mounted installation method. That is, the method of installing the door and window frame, and then assembling the glass and opening the fan in the hole of the pre-embedded frame, and the uneven quality of the construction result in difficult performance of the doors and windows. Guarantee. In order to ensure the installation quality of prefabricated building doors and windows, the prefabricated building should be installed and developed as a whole, which inevitably requires new installation methods that differ from the traditional installation methods of doors and windows. As the high temperature steaming process of the assembled PC exterior wallboard will have a great influence on the quality of the doors and windows, the suspension mounting structure of the rear mouth is recommended as a priority. The advantages are simple and reliable installation, easy replacement and avoiding the influence of temperature deformation. Dedicated mounting adapters, special enclosures, etc. can be used. 3.4 Integrated functions of doors and windows In principle, prefabricated building doors and windows should have various functions of traditional transparent enveloping structures, such as lighting, ventilation, etc., and therefore they must have all kinds of necessary properties, such as wind pressure resistance, airtightness, watertightness, and insulation performance. , Shading performance, sound insulation performance, lighting performance, durability, fire performance and so on. Therefore, as with traditional doors and windows, prefabricated building doors and windows should integrate these functions. At the same time, doors and windows are also integrated into the wall as a part, and even integrate newer IoT technology with intelligent door and window systems, benefiting from the factory manufacturing of door and window products. Can be perfectly applied in prefabricated buildings. 3.5 Door and Window Product Informatization Because assembly-type buildings require the use of building information modeling (BIM) technology, assembly-style building doors and windows necessarily require informatization. The first is to establish a unified information platform, which should be able to standardize the company's standardized door and window products for the majority of relevant personnel. The information platform should also provide relevant grid diagrams and performance parameters for doors and windows. The related grid diagrams will be used to establish the building information model (BIM); at the same time, the platform should provide physical performance data for different window types and different sizes of doors and windows, which can be easily used in combination with standards and design requirements. 4 Problems Prefabricated buildings are in the ascendant in China. Whether it is policy encouragement, government promotion, or the joint efforts of the industry, it is one of the major development directions in the field of construction. Its advantages are obvious. However, as one of the important components in a building, how to adapt to its development, there are still many difficulties to overcome. 4.1 The standard system is not perfect The imperfections of the standard system are manifested in two aspects: First, the standard system of fabricated buildings is not perfect; second, the standard system of windows and doors that are suitable for assembly buildings is not perfect. Assembled buildings currently have only a few architectural and technical standards at the national level. They are all macro-guided standards and lack the support for specific standards such as design, manufacturing, construction, and acceptance. The door and window standard of English assembly building is currently lacking the corresponding technical standards in terms of design, manufacture, installation, and acceptance, in addition to the only few modular coordination standards for the entrance. In this context, the Chinese Academy of Building Research also applied for the Association's standard "Technical Specification for Assembled Building Doors and Windows" and it has already been established. This regulation specifies the doors and windows that are suitable for assembly building in this context. 4.2 Low standardization of doors and windows At present, the standardization of doors and windows in our country is limited to the standardization of materials and accessories. The standardization of doors and windows used in the engineering field is still far from enough. The main reason is that the standardization of the size of doors and windows of Chinese buildings under the traditional model has not been completed. Under the traditional building mode, due to the large randomness of the window size and grid design and the large deviation of the construction of the opening, the door and window companies must review the hole size one by one on the spot and cannot produce and process the given size according to the drawings, and due to too many dimensions Lead to large-scale production. Only a few large real estate development companies have achieved a certain degree of standardization of doors and windows internally, but it is not enough for the entire country level. 4.3 Applicability of door and window production and installation processes to various fabricated structures Prefabricated buildings require major changes in the way doors and windows are manufactured and installed. At present, many prefabricated building doors and windows still adopt the traditional installation method, that is, the factory only pre-embeds the frame, frame, and glass to install on the site one after another. Strictly speaking, this traditional manufacturing and installation method is contrary to the prefabricated building concept; R&D The new type of frame and mounting adapter structure for the integral installation of doors and windows will be the focus of prefabricated building doors and windows. 4.4 Adjustment of New Industry Chain Assembled building doors and windows require product serialization, manufacturing industrialization, construction and assembly, functional integration and product informationization, which will inevitably lead to a new round of reshuffle in the building doors and windows industry. Companies with strong R&D strength and quick adjustments to their ideas will have to grow exponentially in the short term after they have taken the lead in completing adjustments to prefabricated buildings. Most companies are facing closures or becoming foundry positions. There will inevitably be several big brand companies almost monopolizing the entire market.
Particle Board is mainly used for furniture and carriage of bus, train.The bace&back are the Veneer surface, such as Okoume, Bintangor, Pine, Birch, Poplar, Pencil cedar, Maple, Cherry, White Oak, Sapele, Beech, Red Oak, Ash etc.Melamine paper is the most popular to be as the face board, it is abrasion resistant, heat resistant, fouling resistant, clean is simple.The Engineering wood is also as the face and back surface. It is more cheaper and beautiful, can reach the same wood grain effect as the veneer surface.And we have High Quality Particle board.LULI Group Co. Ltd, well known as the leading manufacturer for wooden, steel and paper products, located in Shouguang, Weifang, Shandong, China. Since the foundation in 1985, it focus on the production of Plywood , venner, MDF, particle board, Door skin , Blockboard , Finger joint board, OSB, paper, Steel etc.
Particle board Details:
size:1220*2440MM 1250*2000MM 1525*2440MM 1830*2440MM
THICKNESS:9MM-40MM
MATERIAL:POPLAR, COMBINE, PINE
GLUE:E0, E1, E2
CERTIFICATION:CARB, FSC, CE
Particle board Particle Board,Melamine Particle Board,Particle Board Price,Melamine Laminated Particle Board Luli Group Co.,Ltd. , https://www.plywoods.nl